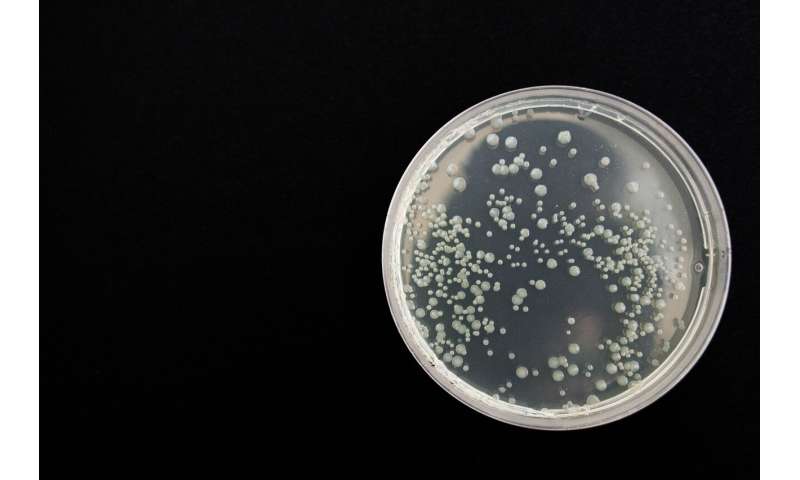
Traditional fluorescent dyes to examine bacteria viability are toxic and suffer poor photostability—but using the VFD has enabled the preparation of a new generation of aggregation-induced emission dye (AIE) luminogens using graphene oxide (GO), thanks to collaborative research between Flinders University's Institute for NanoScale Science and Technology and the Centre for Health Technologies, University of Technology Sydney.
Using the VFD to produce GO/AIE probes with the property of high fluorescence is without precedent—with the new GO/AIE nanoprobe having 1400% brighter high fluorescent performance than AIE luminogen alone.
"It's crucial to develop highly sensitive ways of detecting bacteria that pose a potential threat to humans at the early stage, so health sectors and governments can be informed promptly, to act quickly and efficiently," says Flinders University researcher Professor Youhong Tang.
"Our GO/AIE nanoprobe will significantly enhance long-term tracking of bacteria to effectively control hospital infections, as well as developing new and more efficient antibacterial compounds."
The VFD is a new type of chemical processing tool, capable of instigating chemical reactivity, enabling the controlled processing of materials such as mesoporous silica, and effective in protein folding under continuous flow, which is important in the pharmaceutical industry. It continues to impress researchers for its adaptability in green chemistry innovations.
"Developing such a deep understanding of bacterial viability is important to revise infection control policies and invent effective antibacterial compounds," says lead author of the research, Dr. Javad Tavakoli, a previous researcher from Professor Youhong Tang's group, and now working at the University of Technology Sydney.
"The beauty of this research was developing a highly bright fluorescence dye based on graphene oxide, which has been well recognized as an effective fluorescence quenching material."
The type of AIE luminogen was first developed in 2015 to enable long-term monitoring of bacterial viability, however, increasing its brightness to increase sensitivity and efficiency remained a difficult challenge. Previous attempts to produce AIE luminogen with high brightness proved very time-consuming, requires complex chemistry, and involves catalysts rendering their mass production expensive.
By comparison, the Vortex Fluidic Device allows swift and efficient processing beyond batch production and the potential for cost-effective commercialisation.
Increasing the fluorescent property of GO/AIE depends on the concentration of graphene oxide, the rotation speed of the VFD tube, and the water fraction in the compound—so preparing GO/AIE under the shear stress induced by the VFD's high-speed rotating tube resulted in much brighter probes with significantly enhanced fluorescent intensities.
The paper, "Vortex fluidic enabling and significantly boosting light intensity of graphene oxide with aggregation induced emission luminogen," by Javad Tavakoli, Nikita Joseph, Clarence Chuah, Colin Raston and Youhong Tang—has been published in the journal Materials Chemistry.
Explore further
Citation: 'Unboil an egg' machine creates improved bacteria detector (2020, June 23) retrieved 23 June 2020 from https://ift.tt/37USlf9
This document is subject to copyright. Apart from any fair dealing for the purpose of private study or research, no part may be reproduced without the written permission. The content is provided for information purposes only.
"machine" - Google News
June 23, 2020 at 08:21PM
https://ift.tt/37USlf9
'Unboil an egg' machine creates improved bacteria detector - Phys.org
"machine" - Google News
https://ift.tt/2VUJ7uS
https://ift.tt/2SvsFPt
Bagikan Berita Ini














0 Response to "'Unboil an egg' machine creates improved bacteria detector - Phys.org"
Post a Comment